Parmigiano Reggiano vs. Pecorino Romano: lots of people are still confusing them.
These are two of the most popular cheeses in Italy. Even though they are very similar, there are different things about them that are worth talking about.
For many, these Italian names are too similar and it’s easy to make mistakes. It is also very easy to find products that are passed off as parmesan or pecorino.
So, I thought I’d write this article on the difference between parmesan and pecorino cheese to help you understand what they are, how they are made, what their names mean and where they are produced in Italy.
Parmesan Cheese: What Is It And How Is It Made?
You probably already know what parmesan cheese is.
However, since many people call every kind of Italian dry and hard cheeses by that name, maybe it’s better to start from the basis.
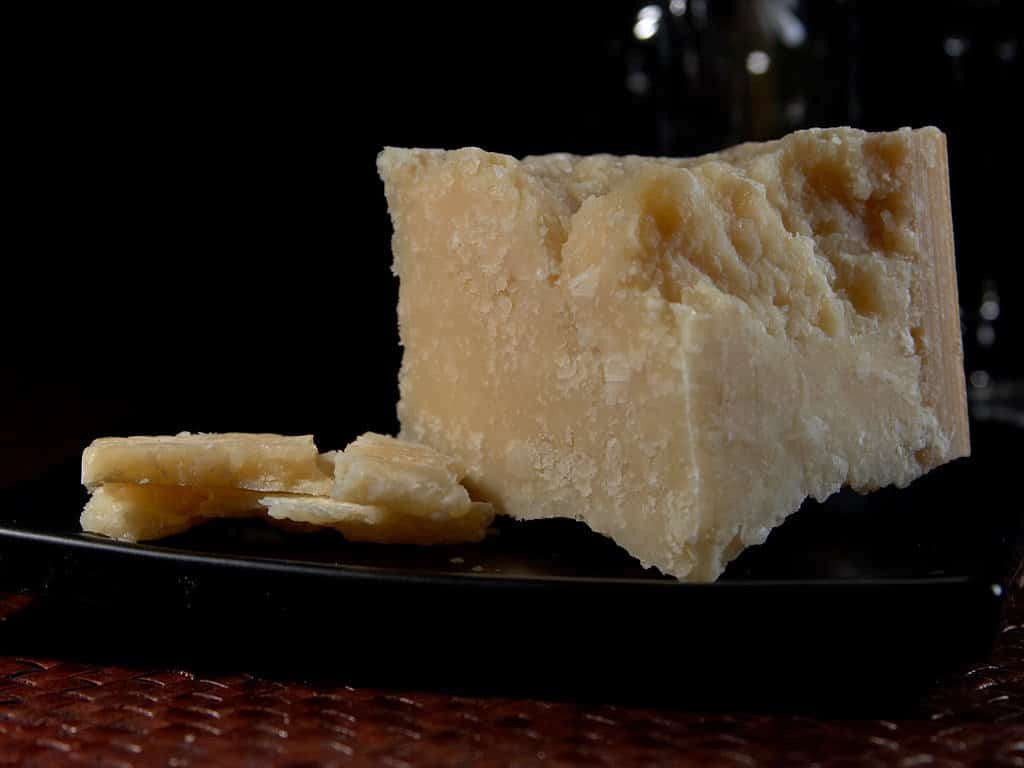
Parmesan cheese, or Parmigiano, is an Italian extra-hard cow’s milk cheese.
Its origins date back to the 12th century, when it was originally produced by Italian monks in Northern Italy. It plays a big part in the rich history of Italian cuisine.
It’s a dry cheese with a granular, crumbly texture, which is why it’s also known as grana.
It has a light straw yellow color that intensifies with aging.
A piece of typical Italian parmesan cheese aged 12-24 months has a fresh, fruity taste with a slightly nutty flavor. The older it gets, the better it tastes.
After 22 months, its flavor profile intensifies and it gets a more granular texture.

What Makes Parmesan Cheese Become Parmigiano Reggiano?
Parmigiano Reggiano is such a good cheese that it’s known as the King of Cheeses. In order to be labeled as “Parmigiano Reggiano”, parmesan cheese must meet specific protected designation of origin (PDO) requirements.
The true Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese can only be produced in the Italian provinces of Bologna, Mantua, Padua and, of course, Parma and Reggio Emilia (to which it owes its name).
Its PDO requirements are very strict and include shape, fat and crust percentage, weight, cows’ feeding, milking process, storage, and aging.
The real deal Parmigiano Reggiano must age for at least 12 months to meet the PDO status.
In many cases the aging process can be up to 24 months.
Are US-made Parmesan Cheeses Different?
Many cheesemakers in the United States produce parmesan cheeses.
These cheeses are made in accordance with FDA rules, but they don’t meet all the DOP requirements for Parmigiano Reggiano and are usually aged only 10 months.
As a result, they usually taste a little more bitter.
So, if you’re traveling through Italy and you decide to try local parmesan, you might be nicely surprised.
But instead of talking about national differences, why don’t we stick to the topic of this post?
Let’s take a look at Pecorino Romano and see how it’s different from parmesan cheese.

Pecorino Romano: How Is It Different From Parmesan?
The main difference between parmesan and pecorino cheese is the milk with which they’re produced.
While parmesan is made from unpasteurized cow’s milk, pecorino is a sheep’s milk cheese.
Its name is actually a hint: pecora is the Italian word for “sheep”.
There are many types of pecorino cheeses produced in Southern and Central Italy. The most famous Italian sheep’s milk cheeses, however, is by far Pecorino Romano.
Pecorino Romano cheese is much older than parmesan. In fact, it dates back to the ancient times of the Roman Age.
As the name suggests, it was originally made in the rural area that surrounded Rome – the so-called “Ager Romanus“. This is the current Lazio region of Italy.
However, a lot of things have changed since then, and now Pecorino Romano is mostly produced in Sardinia. And of course, it has its own PDO requirements.
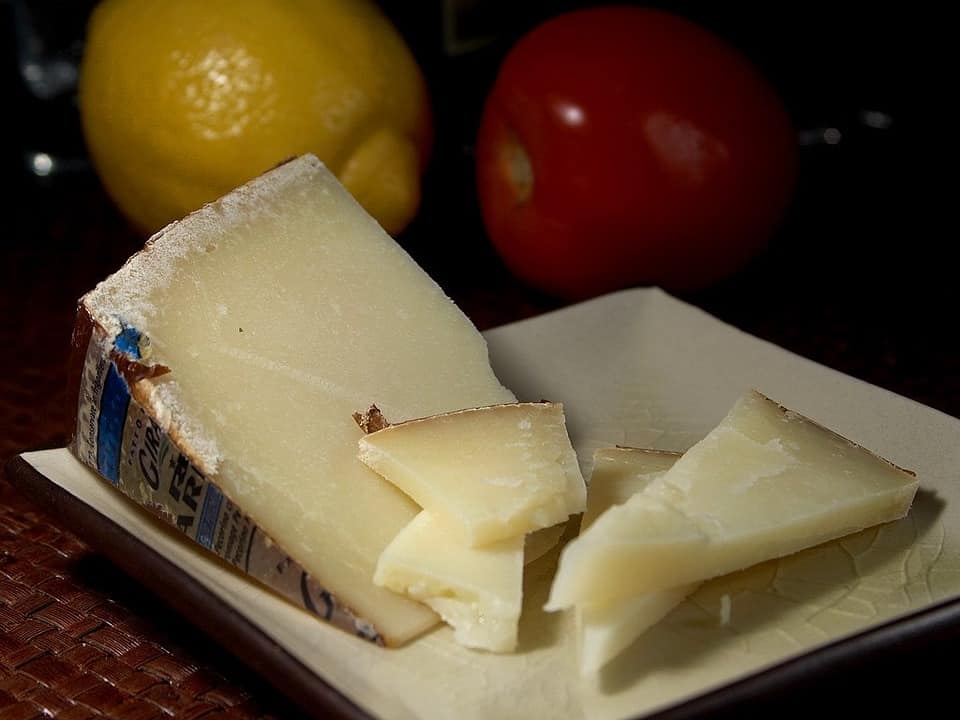

Much like Parmigiano Reggiano, the PDO rules for Pecorino Romano are very strict and cover every aspect of its production, taste, and shape. Pecorino Romano can be produced in Sardinia, Lazio and in the province of Grosseto, using whole fresh milk from local sheep.The first noticeable difference between Pecorino Romano and Parmigiano Reggiano is in their color. Pecorino cheese is typically white and has a brown or black rind. And of course, the sheep’s milk makes it taste very different from parmesan: while the latter is fruity with a nutty taste, pecorino cheese has a spicier, stronger flavor. The people from its regions of production are very fond of it and use it in many traditional recipes.This leads us to another question.

So far, you’ve read all the main technical differences between parmesan and Pecorino Romano.
Now, let’s get to the fun part: which foods should you try them with?
Pecorino Romano vs. Parmigiano: Which Foods Are They Better With?
Both Parmigiano Reggiano and Pecorino Romano are perfect as stand-alone food.
They are salty cheeses that can be enjoyed on a cheese board with a bit of honey and some cured meats.
Thanks to their crumbly structure, they can also be an excellent grating cheese.
However, due to their difference in flavor, they each mix better with some specific plates.
Pecorino Romano has a stronger flavor than parmesan. It originated close to Rome so it’s naturally the best choice for traditional Roman pasta dishes.
The most famous pasta dishes in Rome are pasta all’Amatriciana, Carbonara, spaghetti Cacio e Pepe and Pasta alla Gricia.
Pasta all’Amatricia has a red sauce made with guanciale and tomatoes.
Pasta Carbonara is made with guanciale and eggs.
Cacio e Pepe is a simple pasta dish dressed with pecorino cheese and black pepper.
Finally Pasta alla Gricia is made with pecorino, guanciale and black pepper.
Parmigiano Reggiano, on the other hand, is sweeter than pecorino and should be used to prepare foods like Fettuccine Alfredo, pasta with tomato sauce, risotto, and pasta with ricotta, etc.

Parmesan cheese is also the right choice for every baked pasta dish, like lasagna, eggplant parmigiana, and eggplant involtini.
It can also be used to create a wonderful Parmesan Cream that you can enjoy with all the above-mentioned foods.
If you want to eat it in slices, Parmesan tastes very good with dark chocolate. And if you like truffles, try eating parmesan with truffle honey. It’s to die for!
Finally, there are also recipes that combine these two types of cheese. For instance, the traditional Genoa pesto sauce is made with both Parmigiano Reggiano and Pecorino Romano.
Now that you know the difference between Parmigiano Reggiano and Pecorino Romano and where to use both of them, there’s only one thing left: eat everything. Enjoy!
Pecorino Romano vs. Parmigiano: FAQs
Q: Are Pecorino and Parmesan made from the same kind of milk?
A: Nope! Parmesan is made from cow’s milk, while Pecorino is made from sheep’s milk. That’s part of why Pecorino has a more tangy, earthy flavor.
Q: Is one better for people who are lactose intolerant?
A: Pecorino may be slightly easier to digest for some people with lactose sensitivity, thanks to the sheep’s milk and aging process—but it really depends on the individual. Always check with a doctor if you’re unsure.
Q: Can I use Pecorino instead of Parmesan in recipes?
A: Absolutely—you can swap them, but expect a stronger, saltier bite with Pecorino. If you’re using it in a delicate dish, you might want to use a bit less and taste as you go.
Q: What is Grana Padano cheese?
Grana Padano is similar to Parmigiana Reggiano. It is made in Northern Italian regions in the Po Valley.
Parmesan and Grana Padano are similar cheeses. The key difference is that the production of Grana Padano has less strict guidelines.
An interesting fact is that even though Parmesan and Grana Padano are both “grana” cheeses, the European Union only allows Grana Padano to use the term “grana”.
Q: What are some similarities between Pecorino Romano and Parmigiano?
Despite being different cheeses, Pecorino and Parmesan have a lot in common.
Pecorino Romano and Parmigiano are both hard Italian cheeses. They are also iconic Italian cheeses that you can find at any decent grocery store.
Pecorino and Parmesan are both considered grana cheeses because they have a granular texture.
They are popular grating cheeses and can be found at most pasta dinners.
A salty-flavoured cheese like these will make any simple dish so much better. Sprinkle a little on a chicken parmesan sub and you’ll understand.

I always have a block of Locatelli cheese in my fridge. I recommend it to all of the home cooks out there. You can also buy it already grated.

These cheeses can also be served on a cheese platter and eaten alone.
The salty flavor of these cheeses is nice with a little drizzle of honey.
I don’t consider myself a cheese connoisseur, but I know when I have a little bite of cheese and a sip of wine, it’s the best thing in the world.
Still Torn Between Pecorino vs. Parmesan? Try Both!
At the end of the day, the Pecorino vs. Parmesan debate isn’t about right or wrong—it’s about what tastes best to you and your recipe. Pecorino brings that bold, salty kick, while Parmesan adds a nutty, mellow richness. There’s room in the kitchen (and on your pasta) for both.
Got a favorite way to use one over the other? Drop it in the comments—we’d love to hear from you. And if you’d rather skip the cooking and just enjoy delicious food, visit our store here: https://mortadellaheadstore.com/










6 Responses
Why does pecorino taste saltier?
Because it is salted differently. As far as I know, parmesan cheese is typically left in a solution of water and salt for about twenty days. Pecorino, on the other hand, undergoes the same treatment for a few hours, and is then pierced and rubbed with coarse salt daily for at least a month.
Which one works better in making meatballs?
I’ve always used parmesan cheese in my meatballs, but it really depends on your taste 🙂 You can use both cheeses interchangeably.
Superb article! A few points remain un-answered to me so May I ask; first of all, when added to pasta with the Brine water of the pasta, which of the two is better to emulsify a sauce where I found that Romano gets a bit more gloppy. It may be my problem in application not the cheeses fault. So that’s the first question. Second question is what is the aging of the Romano cheese? is a typically aged as long as the Parmesan, as that may be a factor in the first question regarding emulsification in sauces
Hi Scott. I’m glad you liked my article.
If you’re referring to the type of sauce used for dishes like Cacio e Pepe, Pecorino is the traditional choice. However, you can use both interchangeably. The reason why you’re getting a gloppy sauce could be in the amount of water you’re using or in it’s temperature. I recommend whisking the cheese and water in a separate bowl, starting with a small amount of the latter and adding more later if necessary. Also, not many people say this, but if you want to make things super technical, the water should be cooled down to less than 60°C/140°F. The reason is that if the water is too hot, the cheese will melt completely, while we want it to become creamy.
You don’t need much pasta water for this type of process. When I make cacio e pepe at home, I use espresso cups as measuring tools, and I use just 1 or 2 for 150+ grams of cheese 😀 I save them about 4 minutes before draining the pasta, and I let them cool down aside. Then, I whisk them with the cheese and a fair amount of toasted ground pepper. Make some experiments with small amounts and then expand from there.
About your second question: parmesan cheese is aged for at least 12 months, and usually up to 24 or, in some cases, 36. Pecorino romano, on the other hand, is usually aged for up to 6 or 12 months.
I hope I gave you the answers you needed. Let me know if you have other questions.